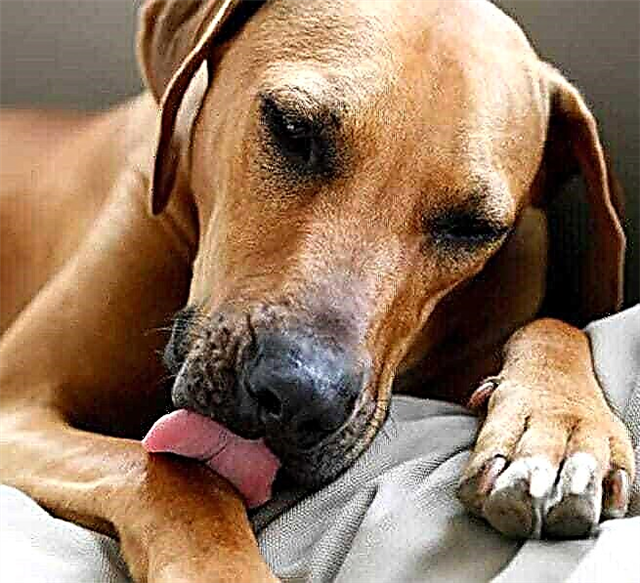
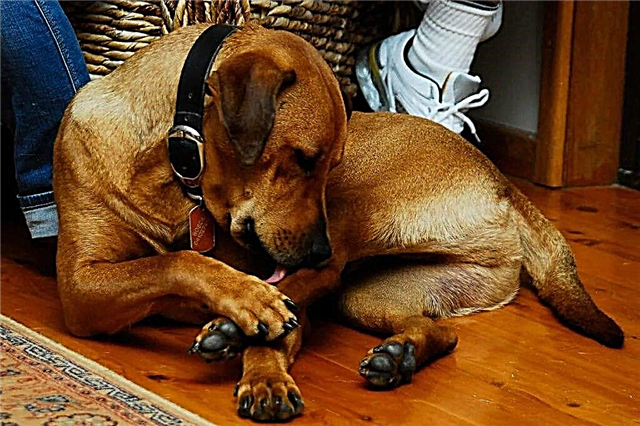
Compulsive behavior characterizes the repeated insurmountable urge to perform some action. That a dog licks or bites itself can be compulsive behavior, because it does not stop doing this.
Why do dogs lick and bite themselves?
All dogs lick and bite themselves from time to time. So they cope with itching. However, if the dog does this too often, it is possible that something is wrong with her. Particular attention should be paid when licking and biting cause hair loss or serious wounds.
Anything that causes itchy skin can lead to problem areas. The most common causes of itching:
- allergy
- parasites
- pain
A bacterial infection appears due to the fact that the dog cannot stop licking and biting itself. Any disease can affect the behavior of the dog. If she licks and bites herself all the time, then she has a reason for this. A visit to the veterinarian will help to understand why the dog exhibits behavior that is harmful to it.
Below are the most common reasons why dogs lick and bite themselves, and tips on how to alleviate their suffering.
Outdoor parasites
Fleas and especially ticks cause excessive itching and discomfort. Check to see if the dog has signs of parasite infection. Comb it with a comb to comb fleas and inspect carefully.You also need to pay attention to whether there are small black spots on the skin. If you suspect that the dog is infected, you should consult your veterinarian about treatment.
Infection

Very often, itching is caused by bacterial and fungal infections. Infections are accompanied by licking and biting, hair loss, peeling of the skin, unpleasant odor and secretions. Excessive scratching of paws and muzzle is characteristic of dogs with bacterial and fungal infections. Regardless of whether it is a bacterial or fungal infection, the dog needs help to cope with it.
Allergy
The most common causes of itching in allergies are insect bites, food allergies, and a reaction to allergens in the environment. Allergies can cause both mild and very severe itching. Contact dermatitis, skin irritation are the result of exposure to an external irritant. Garden plants, lawn chemicals, dust, pollen, mold, cleaning products and cosmetics are just a few of the possible pathogens.
Pain
Something gives the dog physical discomfort. This may be a previous injury or joint damage. Dogs with bone, ligament, or joint damage sometimes lick and bite themselves in pain. The cause may be a small fracture or rupture. The pet may have arthritis, hip dysplasia, or another degenerative condition. If there is a suspicion that the dog is in pain, immediately take her to the veterinarian. The veterinarian will be able to determine the cause of discomfort in a four-legged friend.
Dry skin
Many factors, including cold weather and lack of fatty acids, can cause dry skin in dogs. The dog may respond to discomfort by licking and biting itself. Thyroid dysfunction, nutritional deficiencies and other health problems also cause dry and itchy skin. Nutritional supplements with fatty acids will help to cope with the problem and make the pet's coat healthy.
Hormonal imbalance
If the dog’s body does not produce enough thyroid hormone or secretes too much cortisone, it can start a skin infection. You can notice small red spots on the pet’s body, and it will lick and bite itself, as in an allergy.
Emotional problems
Emotional problems can result from a background illness that causes depression and / or mood disorders. Dogs often lick and bite themselves due to boredom, anxiety, stress, depression, or other nervous shocks. Talk with your veterinarian about all background illnesses that could have caused such an emotional state in your pet.
Itching is a symptom, not a diagnosis or illness, caused by a specific pathogen. The most common causes of itching are parasites, infections, and allergies. There are many skin diseases that do not immediately cause itching. It may appear subsequently due to bacterial or fungal infections. By the time the itch appears, the primary cause may already be gone.
If the itching disappears, then its cause was a microbial infection.However, if the itching does not stop or is only slightly weakened, the dog is most likely allergic to something. Dogs that experience seasonal itching respond to seasonal irritants, and if itching occurs all year, it can be a food allergy.
Excessive amounts of fungi cause very severe itching. If the fungus arose on the paws, the dog will not be able to leave them alone. The same goes for the eyes. The fact that the dog rubs the back of the floor can also be a clue.
The problem area is the part of the skin that becomes inflamed and infected. Affected skin is often red and wet, it releases moisture. She is very sore and itchy. You can also notice the loss of hair. The fact that the dog licks and bites itself only exacerbates the situation.
If the dog licks and bites its paws, it may be allergic. If she licks the paw pads, she probably has a cut or reaction to the chemicals for the lawn.
The veterinarian will help you determine why the dog licks and bites this or that part of the body and prescribes antibiotics, anti-itch drugs or other medications and the necessary treatment in order to alleviate the suffering of the pet.